MLA style is usually used in English and the Humanities. MLA 9th edition uses a citation format for use with ALL source types. MLA 9th edition, updated in 2021, is very similar to the MLA 8th edition from 2016.
Big Picture
In-Text Citations
Use for quotes, paraphrases and summaries
MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics (Purdue OWL)
Work Cited List
MLA Works Cited Page: Basic Format (Purdue, OWL)
These examples, using MLA 8th ed., illustrate the order of information you should include and do not include hanging indents or double spacing. To see sample references on a Works Cited page, view the MLA Sample Paper at Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL).
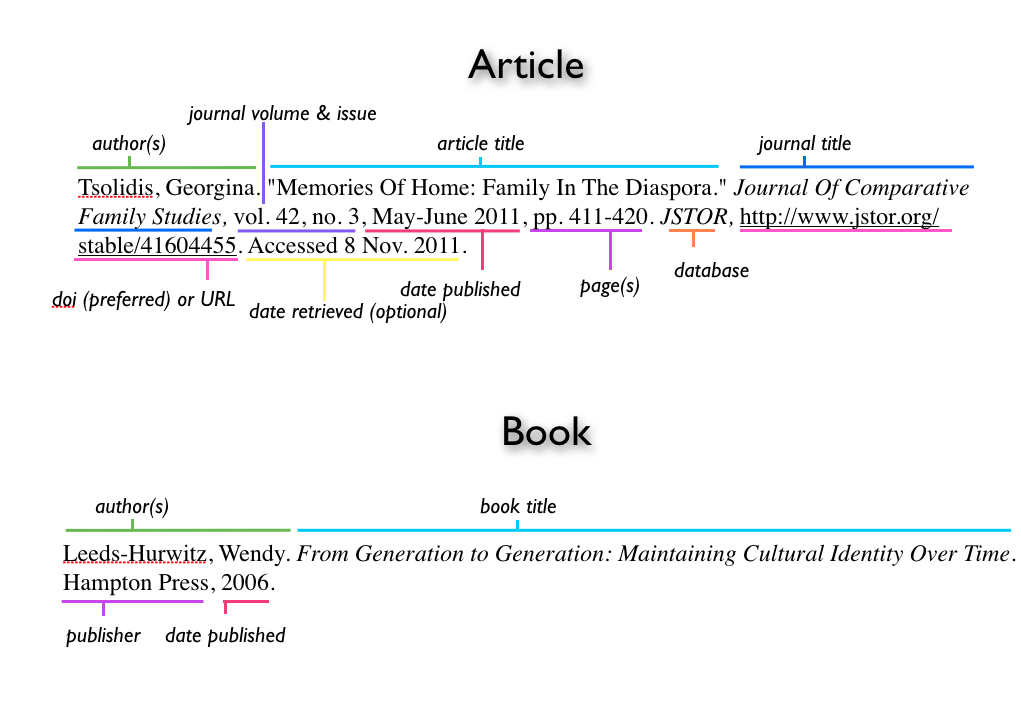
Create citations for your Works Cited page using this template with its elements. Your citation may not include ALL elements. You may also repeat elements 3-9 depending on whether or not your source stands on its own or it is part of one or more containers.
| Order of Elements | Element & Punctuation Following the Element | Example(s) |
| 1 | Author. | |
| 2 | Title of source. | |
| 3 | Title of container, | .... book, journal, database |
| 4 | Other contributors, | Translators or Editors |
| 5 | Version, | Edition |
| 6 | Number, | Vol. and/or No. |
| 7 | Publisher, | |
| 8 | Publication date, | |
| 9 | Location. | Refers to page numbers (pp.) NOT to a place of publication (unless deemed necessary), could refer to a DOI or database URL for an article |
Tips:
Examples of MLA Works Cited: Periodicals (Purdue OWL)